Useful Terminology
- ATC Automatic Tool Changer. A CNC machine feature that automatically changes tools during a machining operation. Consists of a carousel or linear rail with pockets to hold cutting tools.
- Axis A straight line upon which an object moves or rotates
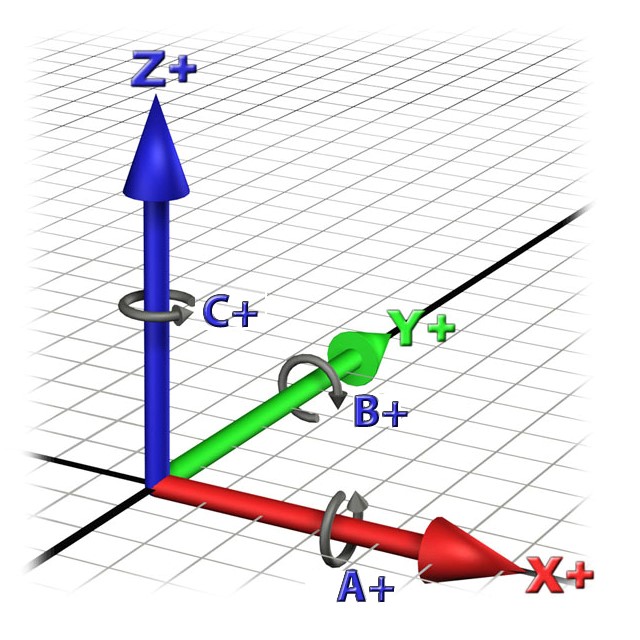
- X – Linear axis representing motions/positions that travel the longest distance parallel to the worktable. (245 mm)
- Y – Linear axis representing motions/positions that travel the shortest distance parallel to the worktable. (110 mm)
- Z – The linear axis that represents motions and positions perpendicular to the worktable. The Z-axis is always parallel to the spindle. (165 mm)
- A – A rotational axis that describes motion around the X-axis. (+/- 180 degrees)
- B – A rotational axis that describes motion around the Y-axis. (+/- 30 degrees)
- CAM Software Specialized Computer Aided Manufacturing software that is used to create programs to be executed by the machine.
- Cartridge Holder for stock material or work pieces that is placed in the fixture.
- Collet Component of the mill that screws into the spindle and holds the cutting tool in place during the machining process. Damaged or worn collets can affect mill performance as they may not be able to grip the tool tight enough, causing excess runout.
- Fixture The mill apparatus that holds inter-changeable material cartridges for various material formats that are to be machined.
- Home Position Location and position of fixture in the center of mill. X, Y, A and B positions are all 0. The spindle is retracted out of the way.
- Jog The mode that allows for the manual operation of tool movement via the jog button generally executed by selecting an axis and a speed or motion increment and then operating the control to move the axis.
- NC File A program generated by CAM software that contains the sets of movement instructions (G-code), tool selection and spindle speed for the machine to follow to create the desired part.
- Runout An inaccuracy of rotating mechanical systems, specifically that the tool or shaft does not rotate exactly in line with the main axis. For example; when drilling, run-out will result in a larger hole than the drill's nominal diameter due to the drill being rotated eccentrically (off axis instead of in line).
- Spindle The main component of the machine tool that rotates. On the machining center, the spindle holds a cutting tool.
- Template A series of machining strategies using various milling tools and cutting parameters that are combined to create a set of instructions for a machine to follow.
- Tool Another term for milling bur, or cutter.
- Tool Holder A small block that holds tools inside the tool changer.
- Strategy Synonymous with template
- Operation A step within a milling strategy/template to perform a single operation
- G-Code Synonymous with NC File or Tape File